Lesson 1 & Part 2
- Introduction to Distributed Computing
- Types of Distributed Systems
- Flynn’s Taxonomy
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
- Message Queueing
- Publish–Subscribe Pattern
- Logical Clocks
Subscribe to get access
Read more of this content when you subscribe today.
Lesson 2 & 3
- Introduction
- Types
- Logical Clocks
- Lamport’s Timestamp
- Vector Clock
- Singhal–Kshemkalyani differential technique
- Fowler–Zwaenepoel’s Direct-Dependency Technique
- Physical Clock Synchronisation
- Causal Ordering
- NTP
Subscribe to get access
Read more of this content when you subscribe today.
Lesson 4
Application vs Control Algorithm Executions
Centralized and Distributed Algorithms
Symmetric vs Asymmetric Algorithms
Anonymous Algorithms
Uniform Algorithms
Adaptive Algorithms
Deterministic vs Non-Deterministic Executions
Execution Inhibition
Synchronous vs Asynchronous Systems
Online vs Offline Algorithms
Failure Models in Distributed Systems
Wait-Free Algorithms
Communication Channels
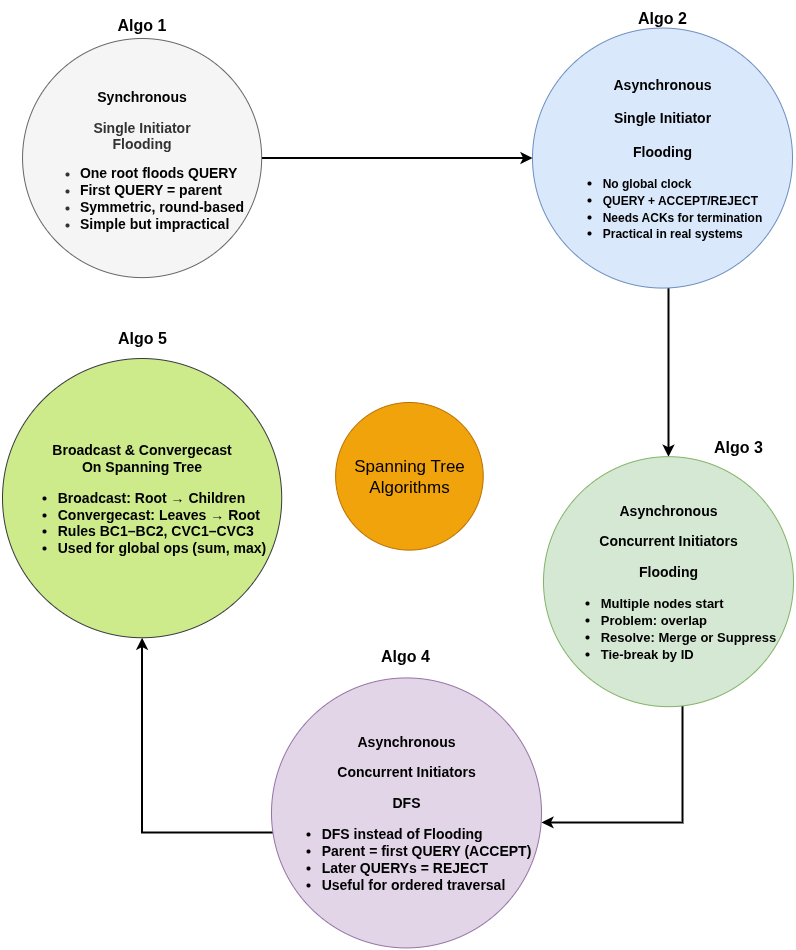
Synchronous Single-Initiator Spanning Tree (Flooding)
Asynchronous Single-Initiator Spanning Tree
Broadcast and Convergecast on a Tree
Memory Map: Algorithms 1–5
Spanning Tree Protocol Memory Map
Lesson 5
Message Ordering and Termination Detection
Message Ordering Paradigms
Asynchronous Executions (Non-FIFO)
Asynchronous Executions (FIFO)
Causally Ordered (CO) Executions
Synchronous Executions (SYNC)
Hierarchy of Orderings
Group Communication
Causal Order (CO)
Causal Order – Examples (violations and satisfactions)
Applications of Causal Ordering
Causal Ordering – Message Delivery
FIFO in Practice
Synchronous Execution (SYNC) (detailed explanation)
Subscribe to get access
Read more of this content when you subscribe today.
Lesson 6
- Message Ordering in Distributed Systems
- Importance of message order for consistency
- Example with replicas
- Total Order
- Definition and need
- Example violation and satisfying scenarios
- Three-Phase Distributed Algorithm
- Purpose (total + causal order)
- Phase 1: Send message
- Phase 2: Collect proposals
- Phase 3: Announce final time
- Nomenclature for Multicast
- Single Source Single Group (SSSG)
- Multiple Sources Single Group (MSSG)
- Single Source Multiple Groups (SSMG)
- Multiple Sources Multiple Groups (MSMG)
- Classification of Application-Level Multicast Algorithms
- Communication history–based algorithms (e.g., Lamport’s timestamps)
- Privilege-based algorithms (token passing)
- Moving sequencer algorithms (with token rotation)
- Fixed sequencer algorithms (centralized sequencer)
- Destination agreement algorithms (timestamp-based and consensus-based)
- Termination Detection
- Importance of detecting termination
- Local vs global termination
- Parallel computations (basic vs control messages)
- Requirements of termination detection algorithms
- Main Termination Detection Approaches
- Using distributed snapshots
- Weight throwing method
- Spanning-tree–based detection
Subscribe to get access
Read more of this content when you subscribe today.

Leave a Reply